Digitalisation in / of Vocational Education and Training
Last November I facilitated a workshop at the European Skills Week event on research in vocational education and training. The workshop was entitled digitalisation in /of vocational education and training. There were some five of us in the workshop and we had about two hours to answer a series of questions based on the following framework.
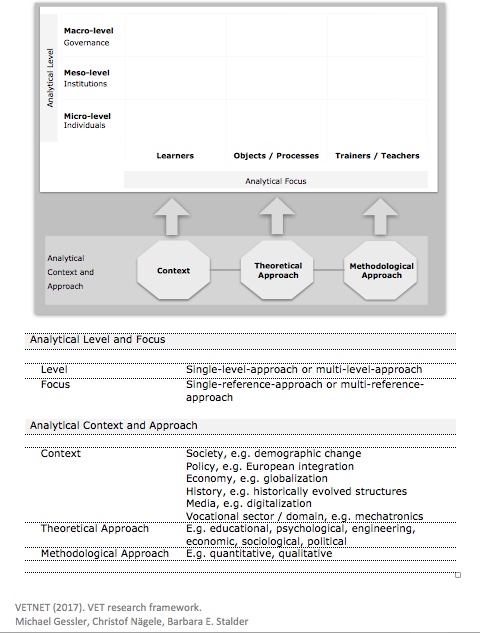
Despite the too short time, I think what we came up with is a good starting point and the discussion will continue in a round table session at the European Conference on Educational Research in Bolzano, Italy in September.
Research Desiderata & Questions
The following central research questions and / or desiderata in this field were identified:
- How do processes of digital transitions and transformations impact on VET and what are the mediation processes and artefacts involved?
- Digital technologies are changing the nature and organisation of work, and the skills and competences required. This is happening simultaneously at a sectoral level and a global level. The new skills and competences are mediated in interactions between different actors but also between actors and objects. These processes of mediation to a large extent shape the practices of using digital technologies.
- In a critical appraisal of digitalisation in VET, what are the different possibilities for the future: What is and more importantly what could be?
- There is a tendency to take technologies and replicate past paradigms – hence for instance the idea of a ‘digital classroom’. Yet digital technologies open new possibilities for vocational education and training. To understand what ‘could be’ requires a critique of existing practices in VET and of the early adoption of technologies for teaching and learning.
- How do digital technologies and transformations affect the creation and meaning of work at a sectoral and global level?
- As technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence are fast being adopted in different sectors and occupations, the future form of work and work organisation is being questioned. Alongside the digital transformations impacting in many sectors, sections of capitalism have advocated digital disruption based on new business models. The use of technology in this way raises Issues of social justice and values. What should be the role of VET in providing the skills and competences to shape the meaning and values of future work and innovation?
Explanation & Justification
Analytical Level
Macro Level
The changing nature of work due to the emergence of new technologies can potentially be shaped. To an extent how technology impacts on work is dependent on values. Equally digital transformations can build on existing skills and competences and older forms of knowledge. To understand these processes requires research at a sector level.
Technological unemployment should not be viewed as simply an issue requiring upskilling, but as questioning forms and organisation of work within society. Life skills are equally important in developing resilience for future employment.
We need a greater understanding of how old knowledge forms are transformed into new knowledge in the digital age.
Meso Level
Institutions mediate processes of skill and competence formation related to digitalisation. What is the relation between specific digital skills required in different sectors and occupations to basic and transversal digital skills? How can skills and knowledge acquired formally or informally in the workplace be linked to education and training in VET institutions.
At the same time, digitalisation provides new possibilities for teaching and learning, for example through augmented reality. This in turn requires the adoption of new pedagogic approaches for VET. Present practices in the adoption of Learning Management Systems form socio-tech systems and may prioritise or marginalise different skills and knowledge.
Micro Level
What are the skills and knowledge required not only to deal with and shape technology in the workplace (in different occupations and sectors) but also for living in the digital age? How does technology transform the work identity of individuals and how do individuals change their own identity for dealing with the changing world of work? What are the life skills that develop the residence required by individuals to deal with digitalisation at a societal level?
Analytical Focus
Learners / Students
Understanding the processes of digital transformation is critical to developing future oriented curricula for learners and students. At the same time, emergent technologies – such as robotics and artificial technologies – call into question existing societal forms of wage labour – once more requiring new curricula for life skills.
We need to focus not only on formal initial training in VET, but on informal learning in the work process leading to identity transformations.
Object / Process
Objects and artefacts play a key role in mediating learning in VET. These artefacts are themselves becoming transformed through digital technologies.
The use of technology opens up new possibilities and contexts for learning, including directly in the workplace. It also potentially empowers processes of social learning, with learners themselves acting as facilitators for other people’s learning and for developing and sharing knowledge within social settings.
This requires research for understanding how such social learning processes can be developed, how new forms of knowledge are acquired and what role objects and artefacts play in these processes.
Trainers / Teachers
There are many examples of good practice in the use of technology for learning in VET and of teachers and trainers sharing knowledge and experiences online. However, many teachers and trainers also feel left behind by the rapid changes in technologies both within occupations and for teaching and training.
Research suggests that best practices are not being generalised because existing models of professional development for teachers and trainers do not scale to meet needs.
An understanding of the possibilities for future VET, requires an understanding by teachers and trainers of the potentials of using technology in their own practice.
