The second in my ‘Rethinking’ series of blog posts. This one – Rethinking e-portfolios’ is the notes for a forthcoming book chapter which I will post on the Wales wide Web when completed..
Several years ago, e-portfolios were the vogue in e-learning research and development circles. Yet today little is heard of them. Why? This is not an unimportant question. One of the failures of the e-learnng community is our tendency to move from one fad to the next, without ever properly examining what worked, what did not, and the reasons for it.
First of all it is important to note that there was never a single understanding or approach to the development and purpose of an e-Portfolio. This can largely due be ascribed to different didactic and pedagogic approaches to e-Portfolio development and use. Some time ago I wrote that “it is possible to distinguish between three broad approaches: the use of e-Portfolios as an assessment tool, the use of e-Portfolios as a tool for professional or career development planning (CDP), and a wider understanding of e-Portfolios as a tool for active learning.”
In a paper presented at the e-Portfolio conference in Cambridge in 2005 (Attwell, 2005), I attempted to distinguish between the different process in e-Portfolio development and then examined the issue of ownership for each of these processes.
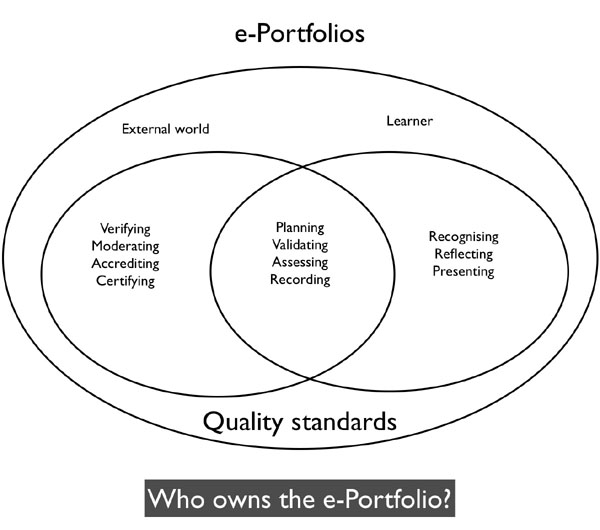
The diagramme reveals not only ownership issues, but possibly contradictory purposes for an e-Portfolio. Is an e-Portfolio intended as a space for learners to record all their learning – that which takes place in the home or in the workplace as well as in a course environment or is it a place or responding to prescribed outcomes for a course or learning programme? How much should a e-Portfolio be considered a tool for assessment and how much for reflection on learning? Can tone environment encompass all of these functions?
These are essentially pedagogic issues. But, as always, they are reflected in e-learning technologies and applications. I worked for a whole on a project aiming to ‘repurpose the OSPI e-portfolio (later merged into Sakai) for use in adult education in the UK. It was almost impossible. The pedagogic use of the e-Portfolio, essentially o report against course outcomes – was hard coded into the software.
Lets look at another, and contrasting, e-Portfolio application, ELGG. Although now used as a social networking platform, in its original incarnation ELGG stared out as a social e-portfolio, originating in research undertaken by Dave Tosh on an e-portfolio project. ELGG essentially provided for students to blog within a social network with fine grained and easy to use access controls. All well and good: students were not restricted to course outcomes in their learning focus. But when it came to report on learning as part of any assessment process, ELGG could do little. There was an attempt to develop a ‘reporting’ plug in tool but that offered little more than the ability to favourite selected posts and accumulate them in one view.
Mahara is another popular open source ePortfolio tool. I have not actively played with Maraha for two years. Although still built around a blogging platform, Mahara incorporated a series of reporting tools, to allow students to present achievements. But it also was predicated on a (university) course and subject structure.
Early thinking around e-Portfolios failed to take into account the importance of feedback – or rather saw feedback as predominately as coming from teachers. The advent of social networking applications showed the power of the internet for what are now being called personal Learning networks, in other words to develop personal networks to share learning and share feedback. An application which merely allowed e-learners to develop their own records of learning, even if they could generate presentations, was clearly not enough.
But even if e-portfolios could be developed with social networking functionality, the tendency for institutionally based learning to regard the class group as the natural network, limited their use in practice. Furthermore the tendency, at least in the school sector, of limited network access in the mistaken name of e-safety once more limited the wider development of ‘social e-Portfolios.”
But perhaps the biggest problem has been around the issue of reflection. Champions have lauded e-portfolios as a natural tools to facilitate reflection on learning. Helen Barrett (2004) says an “electronic portfolio is a reflective tool that demonstrates growth over time.” Yet are e-Portfolios effective in promoting reflection? And is it possible to introduce a reflective tool in an educations system that values the passing of exams through individual assessment over all else? Merely providing spaces for learners to record their learning, albeit in a discursive style does not automatically guarantee reflection. It may be that reflection involves discourse and tools for recording outcomes offer little in this regard.
I have been working for the last three years on developing a reflective e-Portfolio for a careers service based din the UK. The idea is to provide students an opportunity to research different career options and reflect on their preferences, desired choices and outcomes.
We looked very hard at existing opens source e-portfolios as the basis for the project, nut could not find any that met our needs. We eventually decided to develop an e-Portfolio based on WordPress – which we named Freefolio.
At a technical level Freefolio was part hack and part the development of a plug in. Technical developments included:
- The ability to aggregate summaries of entries on a group basis
- The ability add custom profiles to see profiles of peers
- Enhanced group management
- The ability to add blog entries based on predefined xml templates
- More fine grained access controls
- An enhanced workspace view
Much of this has been overtaken by subsequent releases of WordPress multi user and more recently Buddypress. But at the time Freefolio was good. However it did not work in practice. Why? There were two reasons I think. Firstly, the e-Portfolio was only being used for careers lessons in school and that forms too little a part of the curriculum to build a critical mass of familiarity with users. And secondly, it was just too complex for many users. The split between the front end and the back end of WordPress confused users. The pedagogic purpose, as opposed to the functional use was too far apart. Why press on something called ‘new post’ to write about your career choices.
And, despite our attempts to allow users to select different templates, we had constant feedback that there was not enough ease of customisation in the appearance of the e-Portfolio.
In phase two of the project we developed a completely different approach. Rather than produce an overarching e-portfolip, we have developed a series of careers ‘games; to be accessed through the Careers company web site. Each of the six or so games, or mini applications we have developed so far encourages users to reflect on different aspects of their careers choices. Users are encouraged to rate different careers and to return later to review their choices. The site is yet to be rolled out but initial evaluations are promising.
I think there are lessons to be learnt from this. Small applications that encourage users to think are far better than comprehensive e-portfolios applications which try to do everything.
Interestingly, this view seems to have concur with that of CETIS. Simon Grant points out: “The concept of the personal learning environment could helpfully be more related to the e-portfolio (e-p), as both can help informal learning of skills, competence, etc., whether these abilities are formally defined or not.”
I would agree: I have previously seen both as related on a continuum, with differing foci but similar underpinning ideas. However I have always tended to view Personal Learning Environments as a pedagogic capproach, rather than an application. Despite this, there have been attempts to ‘build a PLE’. In that respect (and in relation to rethinking e-Portfolios) Scott Wilson’s views are interesting. Simon Grant says: “As Scott Wilson pointed out, it may be that the PLE concept overreached itself. Even to conceive of “a” system that supports personal learning in general is hazardous, as it invites people to design a “big” system in their own mind. Inevitably, such a “big” system is impractical, and the work on PLEs that was done between, say, 2000 and 2005 has now been taken forward in different ways — Scott’s work on widgets is a good example of enabling tools with a more limited scope, but which can be joined together as needed.”
Simon Grant goes on to say the ““thin portfolio” concept (borrowing from the prior “personal information aggregation and distribution service” concept) represents the idea that you don’t need that portfolio information in one server; but that it is very helpful to have one place where one can access all “your” information, and set permissions for others to view it. This concept is only beginning to be implemented.”
This is similar to the Mash Up Personal Learning Environment, being promoted in a number of European projects. Indeed a forthcoming paper by Fridolin Wild reports on research looking at the value of light weight widgets for promoting reflection that can be embedded in existing e-learning programmes. This is an interesting idea in suggesting that tools for developing an e-Portfolio )or for that matter, a PLE can be embedded in learning activities. This approach does not need to be restricted to formal school or university based learning courses. Widgets could easily be embedded in work based software (and work flow software) and our initial investigations of Work Oriented Personal Learning Environments (WOMBLES) has shown the potential of mobile devices for capturing informal and work based learning.
Of course, one of the big developments in software since the early e-Portfolio days has been the rise of web 2.0, social software and more recently cloud computing. There seems little point in us spending time and effort developing applications for students to share powerpoint presentations when we already have the admirable slideshare application. And for bookmarks, little can compete with Diigo. Most of these applications allow embedding so all work can be displayed in one place. Of course there is an issue as to the longevity of data on such sites (but then, we have the same issue with institutional e-Portfolios and I would always recommend that students retain a local copy of their work). Of course, not all students are confident in the use of such tools: a series of recent studies have blown apart the Digital Native (see for example Hargittai, E. (2010). Digital Na(t)ives? Variation in Internet Skills and Uses among Members of the “Net Generation”. Sociological Inquiry. 80(1):92-113). And some commercial services may be more suitable than other for developing an e-Portfolio: Facebook has in my view limitations! But, somewhat ironically, cloud computing may be moving us nearer to Helen Barrett’s idea of an e-Portfolio. John Morrison recently gave a presentation (downloadable here) based on his study of ‘what aspects of identity as learners and understandings of ways to learn are shown by students who have been through a program using course-based networked learning?’ In discussing technology he looked at University as opposed to personally acquired, standalone as opposed to networked and Explored as opposed to ongoing use.
He found that students:
Did not rush to use new technology
Used face-to-face rather than technology, particularly in early brainstorming phases of a project
Tried out software and rejected that which was not meeting a need
Used a piece of software until another emerged which was better
Restrained the amount of software they used regularly to relatively few programs
Certain technologies were ignored and don’t appear to have been tried out by the students
Students used a piece of software until another emerged which was better which John equates with change. Students restrained the amount of software they used regularly to relatively few programs which he equates with conservatism
Whilst students were previously heavy users of Facebook, they were now abandoning it. And whilst there was little previous use of Google docs, his latest survey suggested that this cloud application was now being heavily used. This is important in that one of the more strange aspects of previous e0Portolio development has been the requirement for most students to upload attached files, produced in an off line work processor, to the e-Portfolio and present as a file attachment. But if students (no doubt partly driven by costs savings) are using online software for their written work, this may make it much easier to develop online e-portfolios.
John concluded that :this cohort lived through substantial technological change. They simplified and rationalized their learning tools. They rejected what was not functional, university technology and some self-acquired tools. They operate from an Acquisition model of learning.” He concluded that “Students can pick up and understand new ways to learn from networks. BUT… they generally don’t. They pick up what is intended.” (It is also well worth reading the discussion board around John’s presentation – – although you will need to be logged in to the Elesig Ning site).
So – the e-Portfolio may have a new life. But what particularly interests me us the interplay between pedagogic ideas and applications and software opportunities and developments in providing that new potential life. And of course, we still have to solve that issue of control and ownership. And as John says, students pick up what is intended. If we continue to adhere to an acquisition model of learning, it will be hard to persuade students to develop reflective e-Portfolios. We should continue to rethink e-Portfolios through a widget based approach. But we have also to continue to rethink our models of education and learning.

