25 years working with Graham Attwell – networking, social media and new challenges
Some time ago it has crossed my mind that i should write some lines on my cooperation with Graham Attwell. Indeed, I have already written a blog post on my 25 years’ journey with European cooperation project and how that journey was continued when I was employed by our research insitute ITB. However, that post was written from my perspective – as a personal learning journey with interruptions and catching up with the momentum. Now I feel the need to take a fresh look from the perspective of working and learning together with Graham Attwell. I guess that the best way is to discuss three themes – networking, social media and facing new challenges.
Networking the networks: community-building across European projects
Our cooperation started in the beginning of the year 1996. I was working as a project manager of Cedefop (European Centre for Development of Vocational Training) and started an activity that was based on accompaniment of European cooperation projects. Graham had moved to Bremen to coordinate the newly started project Europrof – training of new vocational education and training (VET) professionals. The kick-off meeting of that project was the first one that I observed during my accomanaying visits. From the very beginning we saw that we were on the same wave length regarding the ideas on collaborative research, learning from each other and supporting community-building among European VET researchers.
Europrof took already some steps to mobilize a wider set of interested researchers into exchanges with its core partners. I did my part when launching the European seminars of my Cedefop project with partner institutes in Denmark, the Netherlands, Germany, Finland and Portugal. In addition, we initiated several symposia at the European Conferences on Educational Research (ECER) in Sevilla (1996), Frankfurt (1997), Ljubljana (1998), Lahti (1999) and Edinburgh (2000). With these events we promoted learning from each other and joint knowledge development across parallel European projects. Some of the events gave an opportunity to have a closer look at national pilot projects and new initiatives to promote digital competences in the field of VET. As such I remember the 1998 event with Modellversuch Schwarze Pumpe and the joint seminar in 2000 with the Portuguese national Agency Inofor in Sintra. Later on, a major arena for such network-based knowledge sharing emerged as the network-project Forum (funded by the EU 4th Framework Programme for Research). Furthermore, some of these community-building activities were taken up in certain VET-related conferences under the auspices of the current EU presidency. In this respect I remember conference of the Dutch EU presidency 1997 as well as the conferences of the UK and Austrian presidencies in the year 1998. But – all this had its time. The high season of ‘learning from each other’ and ‘networking the networks’ was soon over and the policy climate changed to other directions – and that had consequences for the funding of European projects.
Digital competences and social media in the field of VET
When some of the earlier themes of European projects started to fade away from the European policy agenda, it was important that Graham was active as an explorer on the theme ‘use of ICT in the field of VET‘. His pioneering contribution was the Cedefop-funded digital resource base “ICT in VET”. It was an outcome of intensive networking with other experts and a predecessor of several later community portals (some of which were rather short-lived and some more sustainable). At that time the discussion on promoting digital competences was heavily overshadowed by the hype around eLearning and by enthusiasm on informal ‘career spaces’ of ICT companies. At this phase Graham represented a well-grounded position that ICT competences are to be promoted in substantial vocational learning contexts.
However, at that time the European funding programmes did not focus that strongly on the field of VET. Instead, more overarching interests on ‘lifelong learning’ or on ‘human resources’ were pushed forward. Alongside these, some new priorities started to emerge – such as ‘open source software’ and ‘open educational resources’. Graham was one of the pioneers with these themes. Together with his fellow pioneers he launched network-based projects like SIGOSSEE (Special interest group for open source software in education in Europe) or the ‘Bazaar’ (for promoting open educational resources via the stalls of the Bazaar). At that time he was also a well-known blogger with his “Wales-Wide-Web’.
At this time I had had a career break after leaving Cedefop. Keeping contact with these initiatives helped me to get back on board – in particular when I was employed by the research institute ITB of the University of Bremen. At that time Graham was working closely with ITB (as a Visiting Fellow) and I could follow his new initiatives from a close distance. I also took my first steps as a blogger but that with some tumbling. Firstly I put an emphasis on project-specific blogging on project websites. These turned out to be short-lived activities – when the projects were finalised, the websites were archived and soon the domain-names expired. Another effort was to develop conference blogs for the VETNET network program at the ECER. This turned out to be a lonely job – also these faded away soon. With my personal blog on the Pontydysgu site (thanks to support from Graham) I had difficulties in keeping myself active. In the meantime Graham was roaming across a wider range of projects and had a lot to share and comment on his themes.
Facing new challenges – the Learning Layers project
All this comes together in my mind when I think of the period when we worked together in the EU-funded project Learning Layers (2012 – 2016) and its follow-up phase. The project was originally designed by educational technologists, computer scientists software and developers with whom Graham had worked together. For the EU FP7 (7th Framework Programme of Research, Technology and Development) they had initiated a new project that sought to bring their expertise together to support the introduction of new ICT tools to support (informal) learning in SMEs. The initial idea was to focus on the healthcare sector – notably on networks of GP practices in the Leeds-Bradford region. But the aim was to scale up the innovations Europe-wide by approaching similar SME clusters.
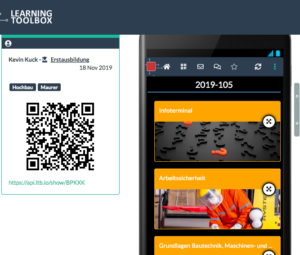
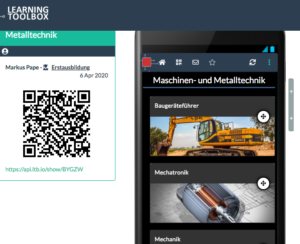
Thanks to Graham, the plan was broadened by introducing a new pilot sector – construction industries and trades from Germany. And that brought our research institute (ITB) into picture as provider of research-based support for the sectoral partners in Germany. And – when working with training centres and SMEs in the construction sector – we were in the need to look closer, how to introduce new ICT tools to support work process-oriented learning. Thus, we were in the middle of promoting the development of digital tools to enhance apprentice training, organisational learning and continuing professional development. And in this context we were able to push forward the co-design process that led to the introduction of the Learning Toolbox (LTB). And, as regular readers of this blog know, we were able to finalise the project with a viable end product that found new uses beyond the initial pilot context.
However – paradoxically – the real success story of the LTB took off in completely different context. Here we need to thank the partners of the project who took the main responsibility of the development of the LTB and promoted it as a support tool for online conferences. a new But, also we in ITB could also draw important lessons from this experience with a major project. For me, the work in the project gave me the boost to become an active blogger. And because of my regular blogging, the progress in the construction pilot could be summarised and reflected on annual basis, in the final phase and during the follow-up activities.
—
I guess this is enough of our journey together with European projects, networks and challenges with digital tools. I have gone to retirement, whilst Graham keeps working with new projects. I wish him and his partners good luck!
More blogs to come …