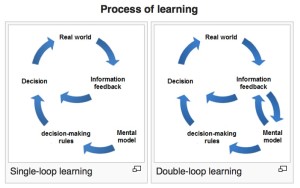
Sometimes writing reports for European projects can be a chore. Long, boring and nobody reads them. At the moment I am writing sections for the EmployID project second annual report. Instead of writing individual work package reports, as is the normal convention, we are writing a single report in the form of a book. And that provides more incentive to get it right. Plus the sections I am writing are all difficult – social learning, Learning Analytics and Labour Market Information tools, but are making me think. So I am quite enjoying it – I think. This last two weeks I have been working on design – or more specifically design for learning. How can we develop designs for tools to support informal learning in public service organisations. I am going to publish here a short series of posts outlining the way I am thinking. I am not sure if this stuff is write but would appreciate any feedback. The first post, today is about practice. Tomorrow I iwll look at the idea of Design Patterns and follow that up on Friday with a draft of a design pattern for Labour market Information tools.
Social Learning
EmployID aims to support and facilitate the learning process of Public Employment Services (PES) practitioners in their professional identity transformation process. The aims of the project are born out of a recognition that to perform successfully in their job they need to acquire
a set of new and transversal skills, develop additional competencies, as well as embed a professional culture
of continuous improvement. However it is unlikely that training programmes will be able to provide sufficient opportunities for all staff in public employment services, particularly in a period f rapid change in the nature and delivery of such services and in a period with intense pressure on public expenditures. Therefore the EmployID project aims to promote, develop and support the efficient use of technologies to provide advanced coaching, reflection and networking services through social learning. The idea of social learning is that people learn through observing others behaviour, attitudes and outcomes of these behaviours, “Most human behaviour is learned observationally through modelling from observing others, one forms an idea of how new behaviours are performed, and on later occasions this coded information serves as a guide for action” (Bandura, 1977). Facilitation is seen as playing a key role in structuring learning and identity transformation activities and to support networking in personal networks, teams and organisational networks, as well as cross-organisational dialogue.
Proposals and initiatives to utilise new technology for learning and professional development in organisations is hardly new. However, a critical review of the way information technologies are being used for workplace learning (Kraiger, 2008) concluded that most solutions are targeted towards a learning model based on the idea of direct instruction. Technology Enhanced Learning initiatives tend to be based upon a traditional business training model transferred from face to face interactions to onscreen interactions, but retaining the standard trainer / learner relationship and a reliance on formal and to some extent standardised course material and curricula.
Research suggests that much learning that takes place in the workplace and through work processes, is multi episodic, is often informal, is problem based and takes place on a just in time basis (Attwell 2007; Hart, 2011). Rather than a reliance on formal or designated trainers, much training and learning involves the passing on of skills and knowledge from skilled workers (Attwell and Baumgartl, 2009). In other words, learning is both highly individualized and heavily integrated with contextual work practices and is inherently social in its nature.
To succeed in supporting identity transformation it is not enough merely to develop or deploy technologies which support training and information transmission. Rather, EmployID needs to develop approaches and pedagogies which can support social facilitation services within PES organisations and which empower individuals to engage in peer learning and facilitation around their own practices.
Although there is much research around the use of technology for learning, far less attention has been paid to informal learning and facilitation processes in the workplace. Research around social practice has largely remained the preserve of social science with different approaches based on structuralism, phenomenology and intersubjectivism amongst others. In his paper on theories of social practice, Reckwitz (2002) draws attention to the dual meaning of the English word practice in German.
“Practice’ (Praxis) in the singular represents merely an emphatic term to describe the whole of human action (in contrast to ‘theory’ and mere thinking). ‘Practices’ in the sense of the theory of social practices, however, is something else. A ‘practice’ (Praktik) is a routinized type of behaviour which consists of several elements, interconnected to one other: forms of bodily activities, forms of mental activities, ‘things’ and their use, a background know- ledge in the form of understanding, know-how, states of emotion and motivational knowledge. A practice – a way of cooking, of consuming, of working, of investigating, of taking care of oneself or of others, etc. – forms so to speak a ‘block’ whose existence necessarily depends on the existence and specific inter-connectedness of these elements, and which cannot be reduced to any one of these single elements.
Likewise, a practice represents a pattern which can be filled out by a multitude of single and often unique actions reproducing the practice (a certain way of consuming goods can be filled out by plenty of actual acts of consumption). The single individual – as a bodily and mental agent – then acts as the ‘carrier’ (Träger) of a practice – and, in fact, of many different practices which need not be coordinated with one another. Thus, she or he is not only a carrier of patterns of bodily behaviour, but also of certain routinized ways of understanding, knowing how and desiring. (pp249-250)”
In this understanding knowledge is more complex than ‘knowing that’. It embraces ways of understanding, knowing how, ways of wanting and of feeling that are linked to each other within a practice.
In seeking to support facilitation within public employment services a vital prerequisite is understanding the nature of the social practices within the workplace, both through observable patterns of individual practice and through developing an overall pattern language. This includes the use of objects. Objects are necessary components of many practices – just as indispensable as bodily and mental activities. (Reckwitz, 2002). Carrying out a practice very often means using particular things in a certain way. Electronic media itself is an object which can mold social practices and enable and limit certain bodily and mental activities, certain knowledge and understanding as elements of practices (Kittler, 1985; Gumbrecht, 1988). One approach to choosing ways to develop particular objects is to focus on what Onstenk (1997) defines as core problems: the problems and dilemmas that are central to the practice of an occupation that have significance both for individual and organisational performance.
If understanding the nature of social practices and patterns is a necessary step to developing facilitation services, it is not in itself sufficient. Further understanding is needed of how learning, particularly informal learning, takes place in the workplace and how knowledge is shared and developed.
Michael Eraut (2000) points put that “much uncodified cultural knowledge is acquired informally through participation in social activities; and much is often so ‘taken for granted’ that people are unaware of its influence on their behaviour. This phenomenon is much broader in scope than the implicit learning normally associated with the concept of socialisation. In addition to the cultural practices and discourses of different professions and their specialities, one has to consider the cultural knowledge that permeates the beliefs and behaviours of their co-workers, their clients and the general public.”
Eraut attempts to codify different elements of practice:
1. Assessing clients and/or situations (sometimes briefly, sometimes involving a long process of investigation) and continuing to monitor them;
2. Deciding what, if any, action to take, both immediately and over a longer period (either individually or as a leader or member of a team);
3. Pursuing an agreed course of action, modifying, consulting and reassessing as and when necessary;
4. Metacognitive monitoring of oneself, people needing attention and the general progress of the case, problem, project or situation.
He also draws attention to the importance of what he calls mediating objects and points out that while some artifacts are used mainly during learning processes, most artifacts used for working are also used for learning. Such artefacts play an important role in structuring work and sharing information and in mediat9ing group learning about clients or projects in progress.
Among informal learning processes that Eraut lists are participation in group processes, consultations, problem solving, trying things out and working with clients. Working alongside others is important in allowing “people to observe and listen to others at work and to participate in activities; and hence to learn some new practices and new perspectives, to become aware of different kinds of knowledge and expertise, and to gain some sense of other people’s tacit knowledge.”
Tackling challenging tasks and roles requires on-the job learning and, if well- supported and successful, leads to increased motivation and confidence.
According to De Laat (2012) informal learning in the workplace is often described as observing how others do things, asking questions, trial and error, sharing stories with others and casual conversation (Marsick and Watkins, 1990). Boud and Hager (2012) argue that learning is a normal part of working and professional development should be placed in a social context where professionals work and learn together, changing and innovating both their professional practice as well as their professional identity.
De Laat (2012) argues that we need to find a new balance between formal and informal learning and provide opportunities for what Fuller and Unwin (2003) call expansive ‐ as opposed to restrictive learning ‐ through developing an organisational culture that values and supports learning and by so doing, opens doors to various opportunities for professional development. Informal professional development through engagement in social learning spaces can enable participation, construction and ‘becoming’ (De Laat, 2012).
Lave and Wenger (1991) also stress the importance of both practice and the social nature of learning in their conception of Communities of Practice. Interestingly for them, collective learning results in practices that reflect both the pursuit of our enterprises and the attendant social relations. “These practices are thus the property of a kind of community created over time by the sustained pursuit of a shared enterprise. It makes sense, therefore to call these kinds of communities communities of practice.”
“Communities of Practice are important to the functioning of any organisations, but they become crucial to those that recognise knowledge as a key asset. An effective organisation comprises a constellation of interconnected CoPs, each dealing with specific aspects of the company’s competency, from the peculiarities of a long standing client, to manufacturing safety, to esoteric technical inventions. Knowledge is created, shared. organised, revised, and passed on within and among these communities.” (Wenger, 1998).
Connecting people in parallel, across disciplines, roles and departments of the business, is fundamentally different from connecting people in project teams or interest groups. Although the nature and composition of these communities varies members are brought together by joining in common activities and by ‘what they have learned through their mutual engagement in these activities’
According to Wenger (1998), a community of practice defines itself along three dimensions:
· What it is about – its joint enterprise as understood and continually renegotiated by its members.
· How it functions ‐ mutual engagement that bind members together into a social entity.
· What capability it has produced – the shared repertoire of communal resources (routines, sensibilities, artefacts, vocabulary, styles, etc.) that members have developed over time. (Wenger, 1998)
A number of issues emerge in studies of attempts to develop communities of practice. One is a tendency to build a platform and ‘declare’ the existence of a community of practice, rather than supporting emergence and therefore ownership. The second is to fail to recognise that such a process of emergence is continuous and ongoing. A third is to conflate organisational structures with communities and to focus on the organisational nature of the community rather than the routines and artefacts that define the capability of practices.
In a similar way social learning is not something which can be done to people. Instead an approach to social learning has to be based on facilitation of social learning processes with organisations and within Communities of Practice. Such facilitation needs to relate to the social practices of people. Murphy (2004) has conceptualized collaboration as a continuum of processes, and developed an instrument with six stages for the purpose of identifying and measuring online asynchronous collaboration: “(1) social presence (2) articulating individual perspectives (3) accommodating or reflecting the perspectives of others (4) co-constructing shared perspectives and meanings (5) building shared goals and purposes, and (6) producing shared artefacts.” However, these six stages can also serve as a template for social learning processes and inform the work of EmployID in developing tools which can facilitate social learning.
References
Attwell, G. (ed.) (2007). Searching, Lurking and the Zone of Proximal Development. E-Learning in Small and Medium Enterprises in Europe, Vol.5, Navreme Publications, Vienna
Attwell, G. & Baumgartl, B. (Eds.) (2009): Creating Learning Spaces: Training and Professional Development for Trainers. Vol.9, Navreme Publications, Vienna
Bandura, A. (1977). Social Learning Theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Boud, D. & Hager, P. (2012). Re-thinking continuing professional development through changing metaphors and location in professional practice. Studies in Continuing Education, 34(1),17-30
De Laat, M. (2012) Enabling professional development networks: How connected are you?, Open University of the Netherlands, Hagen
Eraut, M. (2000) Non-formal learning and tacit knowledge in professional work, British Journal of Educational Psychology (2000), 70, 113–136
Fuller, A., & Unwin, L. (2003). Learning as apprentices in the contemporary UK workplace: Creating and managing expansive and restrictive participation. Journal of Education and Work, 16(4), 407-42
Gumbrecht, H. U. (Ed.) (1988) Materialität der Kommunikation. Frankfurt/Main: Suhrkamp.
Hart, J. (2011) Learning is more than Social Learning, http://www.elearningcouncil.com/content/social-media-learning-more-social- learning-jane-hart, retrieved 5 July, 2012
Kittler, F. (1985) Aufschreibesysteme 1800/1900. München: Fink.
Kraiger, K. (2008). Transforming Our Models of Learning and Development: Web- Based Instruction as Enabler of Third-Generation Instruction. Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 1(4), 454-467. doi:10.1111/j.1754-9434.2008.00086.x
Lave, J. and Wenger, E. (1991) Situated Learning. Legitimate peripheral participation, Cambridge: University of Cambridge Press,
Marsick, V. J., & Watkins, K. (1990).Informal and Incidental Learning in the Workplace.London: Routledge
Murphy, E. (2004). Recognizing and promoting collaboration in an online asynchronous discussion. British Journal of Educational Technology, 35(4), 421-431.
Onstenk, J. (1997) Lerend leren werken: Brede vakbekwaamheid en de integratie van leren, werken en innovere
Reckwitz A (2002) Toward a Theory of Social Practices, European Journal of Social Theory 2002 5: 243
Tennant, M. (1999) ‘Is learning transferable?’ in D. Boud and J. Garrick (eds.) Understanding Learning at Work, London: Routledge.
Wenger, E. (1999), Communities of Practice. Learning, meaning and identity, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Wenger, E. (1998) ‘Communities of Practice. Learning as a social system’, Systems Thinker,
 EmployID “Supporting learning innovation in European Public Employment Services” is a research project aiming at supporting public employment services and their employees in adapting to the changes to their world of work by facilitating the development of their professional identities.
EmployID “Supporting learning innovation in European Public Employment Services” is a research project aiming at supporting public employment services and their employees in adapting to the changes to their world of work by facilitating the development of their professional identities.

 don’t have the money to pay for fees and travel (let alone beer) in attending these events. I am not sure that I actually miss the conferences themselves, but I do miss meeting friends and catching up with what is going on.
don’t have the money to pay for fees and travel (let alone beer) in attending these events. I am not sure that I actually miss the conferences themselves, but I do miss meeting friends and catching up with what is going on.