Impressive Learning Toolbox Showcase presents the success of ePosters
In my latest blog I had reported of the achievements of our former partners from the Learning Layers (LL) project with ePosters powered by the Learning Toolbox (LTB) in different online conferences. As regular readers of this blog know, the LTB was developed as a digital toolset to support workplace-based and vocational learning in the Construction pilot of the LL project. After the project the LTB-developers have developed a spin-off innovation with ePosters that use the functionality of the LTB. The further development and commercialisation is carried out by the start-up company Kubify BV and up-to-date information is delivered via their Twitter feed Kubify – LTB for ePosters. After I had written my latest post I discovered that the LTB-developers had released a new Learning Toolbox Showcase that presents a gallery of ‘all stars’ of ePosters in recent conferences. Below I will give some insights into this interesting resource environment.
ePosters conquer new grounds
So far I have been able to observe the progress with the LTB-powered ePosters from the conferences of the Association of Medical Educators in Europe (AMEE) in the years 2017 and 2018. I have also become aware that they have been able to mainstream the use of ePosters in several conferences – mainly in the healthcare sector. In my recent blog I referred to the new interest of several conference organisers who have had to transform the conferences into online event. Yet, my picture of the progress has been fragmentary and my awareness of the range of LTB-users has been narrow.
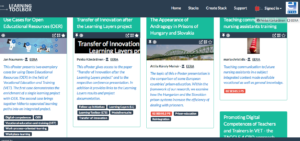
Now, when looking at the selected ePosters of the LTB Showcase I realise, how widely the innovation has spread – both in geographic and in domain-related terms. What is of particular interest, is the fact that some of the early users have incorporated the ePosters into their regular conference culture – no longer as an optional space but as a mainstream approach. Moreover, some of the new users have directly stepped into a broad-based introduction of ePosters. And last but not least – whilst the main activity around the ePosters will take place during the conference dates, the ePosters are visited in great numbers also after the conferences (as the statistics of the LTB-developers show it).
Concerning the spread of the ePosters, this new showcase makes it transparent that they are really widely used in several conferences and online events. In fact, the sample that is presented is merely the top of an iceberg. Behind the chosen ones there is a critical mass of other ones. So, when clicking the names of the events (attached to the ePosters) you will get a link to the respective showcase with many more to explore. Below I try to give a brief group picture.
The ePosters made their breakthrough in conferences of the healthcare sector, in particular addressing educators of healthcare professionals. Already this field brings into picture quite a variety thematic areas:
- AMEE – the annual conference of medical educators in Europe
- ADEE – the annual conference of dentist educators in Europe
- Clinical Education Network Symposium
- SESAM – the conference on simulations in healthcare education
- Future Physiology – the conference of early career researchers of the Physiological Society
In addition to the above-listed regular conferences, ePosters have been used widely in special events focusing on other themes that are related to the healthcare issues, such as:
- Mirots – the multiplier event of the project for internationalisation of occupational therapy
- APS – the conference for plant health
Furthermore, ePosters have been used in other kinds of contexts, such as
- Midlands4Cities Digital Research Festival – a regional R&D festival with a broad variety of topics
- EC-TEL and DELFI Poster and Demo Track – a section in the online conference on technology-enhanced learning
- IMEX Association Day – a discussion group in a conference of event organisers.
ePosters bring richness to knowledge sharing
When looking at the topics covered in the various showcases it is interesting to see different aspects of expertise and professional development being covered by different ePosters. Then, having them arranged as a conceptual neighbourhood in the common showcase, they give a group picture of current progress in the respective online community. And finally, the fact that the ePosters remain accessible in the showcase after the conference, they remain as sustainable knowledge resources that can be reused as support for domain-specific learning.
—
I think that this is enough of the new Learning Toolbox Showcase and of the thematic showcases that provide the background for this ‘all stars’ formation. Altogether I am impressed. And I am eager to learn more, how such ePosters and showcases can be used to support the promotion of digital competences of teachers and trainers.
More blogs to come …






 The UK Centre for Cities has been undertaking a lot of interesting research on the future of cities. In a recent article on their website, they look at ‘why place matters when thinking about productivity. Productivity has been persistently low in the UK and the article discusses “‘Place’, one of the pillars of productivity identified by the
The UK Centre for Cities has been undertaking a lot of interesting research on the future of cities. In a recent article on their website, they look at ‘why place matters when thinking about productivity. Productivity has been persistently low in the UK and the article discusses “‘Place’, one of the pillars of productivity identified by the  Pontydysgu’s Spanish organisation is part of the
Pontydysgu’s Spanish organisation is part of the 
