For some time I have been interested in Entrepreneurship. For one thing I resented the way the Thatcher and Blair acolytes had stolen the word. Working class people have also been entrepreneurial, setting up small businesses or providing services. Yet to listen to the new reasoning, entrepreneurs were the Bill Gates and Steve Jobs of the world, millionaires and directors of multi million pound listed software companies. Just as Puritanism equated being wealthy with being one of the saved, so neo-liberalism equated being rich with being an entrepreneur. It was something the poor should aspire to and they should study in awe rich people as role models.
Since the onset of the recession, or the crisis as it is universally called in southern Europe, some of the gloss has faded at least from the bankers.
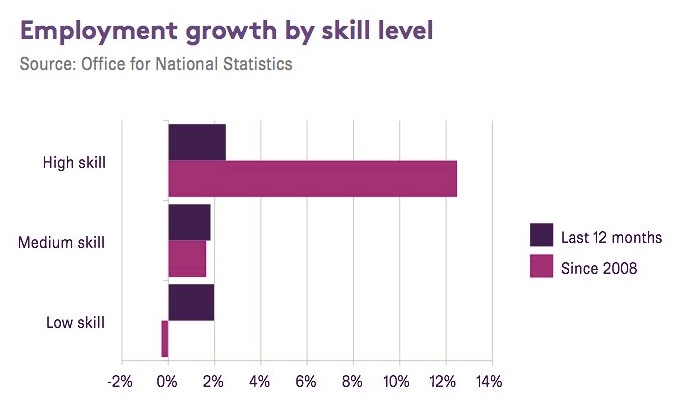
Yet with unemployment and especially youth unemployment remaining at very high levels and with employment increasingly precarious, there seems, at least in Spain where i am living, to be ever more emphasis on entrepreneurship as the hope for the future of employment. Over the last week we have attended two conferences and workshops on innovation and entrepreneurship. On the one hand the increasing support for people trying to set up their own businesses is to be welcomed, even if coordination between the many different agencies involved seems somewhat lacking.
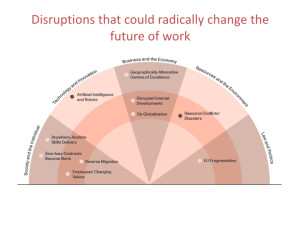
Yet the line of argument seems somewhat under developed. The answer for the ailing labour market is innovation Innovation is connected to entrepreneurship. The great future for innovation is technology in disrupting markets. Universities need to develop closer links to industry. We need more training in technology. Web 2.0 and social media are critical to marketing innovations. Look to Apple, look to Uber, look to AirB. Don’t forget the example of The Great Steve Jobs as a role model. And so on.
As
Jim Groom and Brian Lamb said in 2014 “Today, innovation is increasingly conflated with hype, disruption for disruption’s sake, and outsourcing laced with a dose of austerity-driven downsizing.” And I fear the increasing popularity and support for entrepreneurship is also becoming conflated with hype.
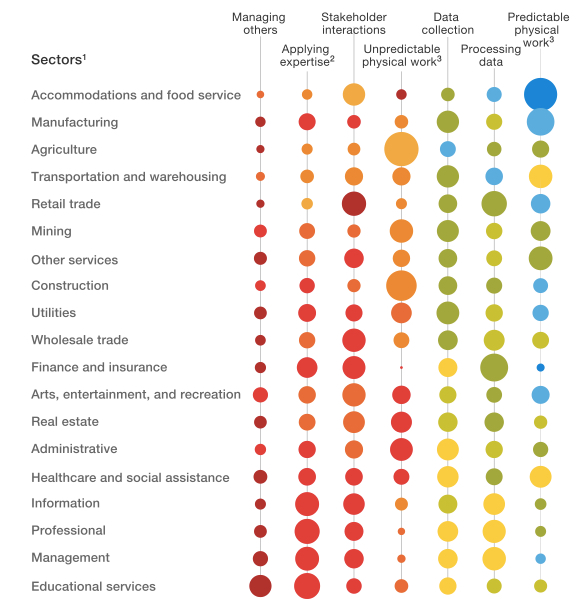
I am curious about the overwhelming emphasis on technology, software and hardware. Is there any city on Spain – or for that matter anywhere else – which is not trying to develop the next Silicon Valley? Yet looking at the figures, the construction and care industries remain two of the largest industries in Europe by numbers employed. Yet they are rarely, if ever, linked to entrepreneurship. Services are continuing to grow in employment, although this covers a wide range of occupations. The number of people who make real money out of releasing Apps to the various app markets is extremely limited.
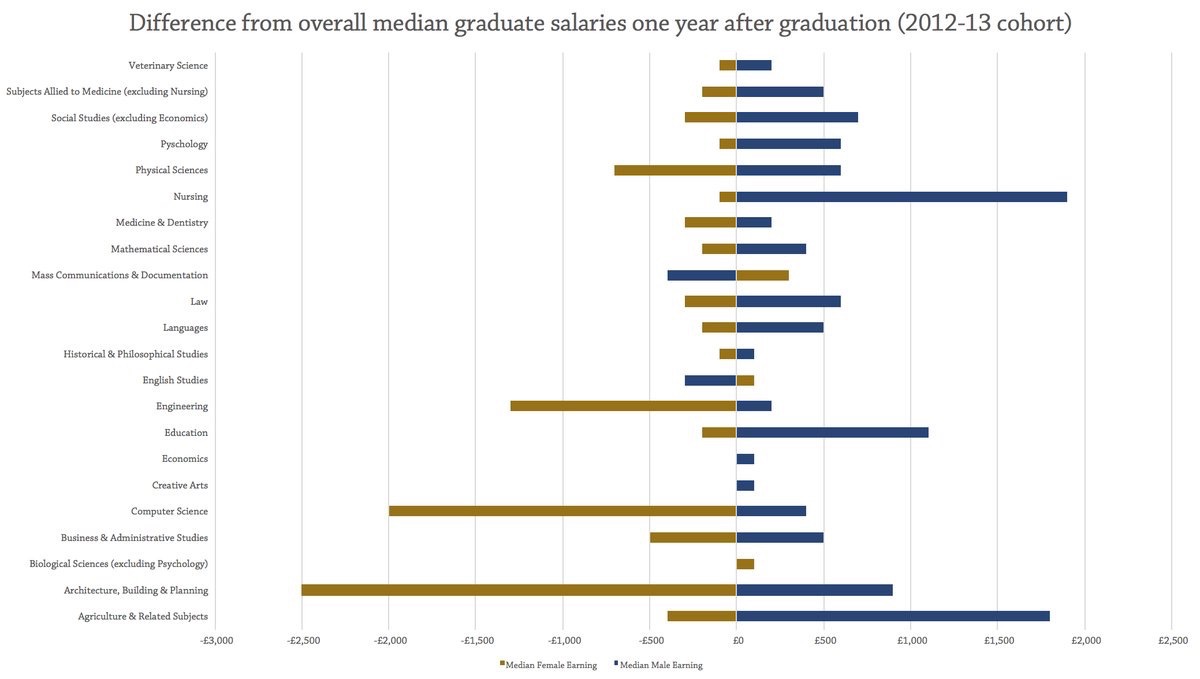
I think we need more nuanced thinking around a number of issues. Clearly labour markets are closely tied to employment. Whatever skills we teach young people they will not gain employment if there are no jobs. Self employment and starting up a business are increasingly attractive routes for young people (especially as there is little alternative). However businesses vary greatly in size and type. Motivations and ambition can be very different. Some people are just looking for a weekend or hobby business, others may be wanting to build on skills. Disruption is probably a minor source of employment or indeed driver of entrepreneurship.
Whilst there is progress in providing support or young people in setting up their own business, advice and help is seldom geared towards them. Being told to go away and produce a profit and loss projection in a spreadsheet is only a small part of the story. And probably the major lack at the moment is help to develop businesses towards sustainability. Growth is not the only measure of sustainability. Bank capital is still in scarce supply and whilst welcome crowd funding has its downsides. And the schooling system in Spain, based on remembering facts, hardly helps young people in striking out on their own.
Above all policy and practice need to link up. Having said that there is a big contradiction between policies of austerity and policies of supporting entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship requires public support as well as private funding. Enough for today…more to come.
 Interest in Vocational Education and Training (VET) seems to go in cycles. Its always around but some times it is much more to the forefront than others as a debate over policy and practice. Given the pervasively high levels of youth unemployment, at least in south Europe, and the growing fears over future jobs, it is perhaps not surprising that the debate around VET is once more in the ascendancy. And the debates over how VET is structured, the relation of VET to higher education, the development of new curricula, the uses of technology for learning, the fostering of informal learning, relations between companies and VET schools, the provision of high quality careers counselling and guidance, training the trainers – I could go on – are always welcome.
Interest in Vocational Education and Training (VET) seems to go in cycles. Its always around but some times it is much more to the forefront than others as a debate over policy and practice. Given the pervasively high levels of youth unemployment, at least in south Europe, and the growing fears over future jobs, it is perhaps not surprising that the debate around VET is once more in the ascendancy. And the debates over how VET is structured, the relation of VET to higher education, the development of new curricula, the uses of technology for learning, the fostering of informal learning, relations between companies and VET schools, the provision of high quality careers counselling and guidance, training the trainers – I could go on – are always welcome.